Several autism tests for children and assessments are available to evaluate behavior, communication skills, and social interaction in children with autism spectrum disorder. These tests help identify the child’s needs and challenges. Based on the results, the developmental pediatrician or therapist guides parents about the most appropriate treatments, such as speech therapy, applied behavior analysis (ABA), sensory integration therapy, or occupational therapy. They also make recommendations focusing on behavioral activities and, if needed, suggest medications like Risperidone. These autism tests play an important role in helping parents work toward improving their child’s independence and life skills.
Table of Contents
Autism tests for children
It is essential to diagnose Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in early childhood because early intervention is crucial for managing behaviors such as communication challenges, social interaction difficulties, and repetitive behaviors.
Some common tests for autistic children are as follows:
1. M-CHAT (Modified checklist for autism in toddlers)
The Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) is a screening tool developed to identify autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children aged 16 to 30 months. It consists of 20 questions focusing on social communication and behavioral development. Parents are required to answer these questions with a “Yes” or “No.
Questions are based on:
- social behavior like eye contact, responding to names, playing with toys, etc.
- communications patterns like Gestures, words, etc.
- Repetitive behaviors like lining up toys, throwing toys again and again, jumping, hopping, etc.
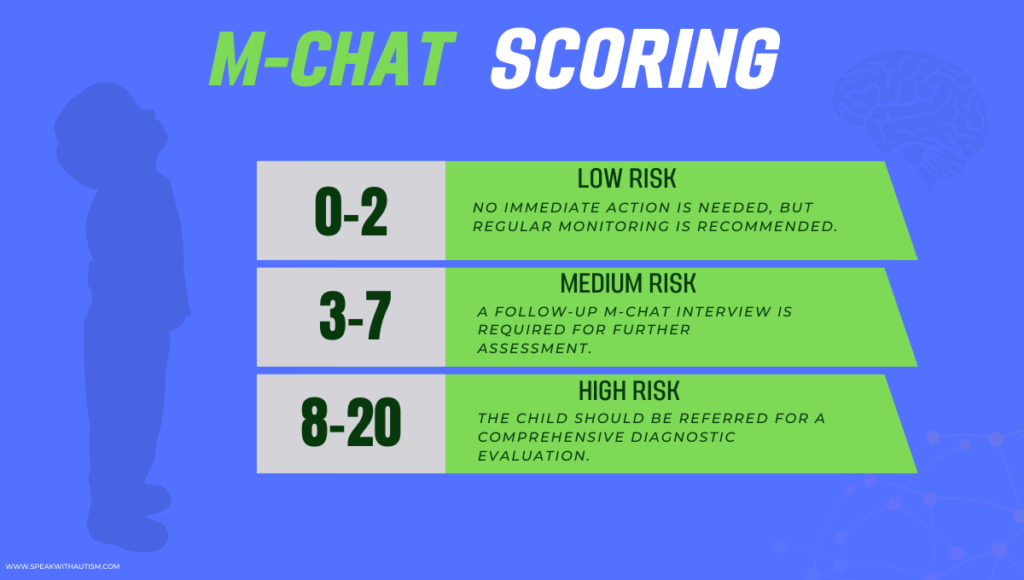
M-CHAT Scoring
In the M-CHAT, a child is scored based on the answers to 20 questions. Each “at-risk” response is given 1 point, and the total score determines the risk level:
- 0-2 Points (Low Risk): No immediate action is needed, but regular monitoring is recommended.
- 3-7 Points (Medium Risk): A follow-up M-CHAT interview is required for further assessment.
- 8-20 Points (High Risk): The child should be referred for a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation.
- This scoring system helps identify the level of risk and guides the next steps for evaluation or intervention.
2. ADOS-2 (Autism diagnostic observation schedule,2nd edition)
ADOS-2 (Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule – Second Edition) is considered the gold standard tool for diagnosing autism. It is typically used when autism symptoms are not clearly evident. The ADOS-2 evaluates children through structured observations and play-based activities. It consists of four different modules, which are selected based on the child’s age and language level. Each module is specifically designed to assess the child’s communication skills and behavioral patterns.
- Module 1: For non-verbal children or those with very minimal speech.
- Module 2: For children with basic speech who use short phrases for communication.
- Module 3: For young children who are fluent in speaking.
- Module 4: For adolescents and adults who are fluent in speaking.
In this test, both adults and children interact with the therapist, and the therapist makes the diagnosis based on their communication and behavior
3. ADI-R (Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised)
This test is conducted when parents feel that their child’s developmental history is concerning or if they suspect autism. It is based on the child’s early development and behavior. In this test, a therapist asks the parents 93 questions, and the parents are required to answer them. The questions cover areas such as communication (e.g., speech milestones), socialization (e.g., social behavior), and repetitive behaviors.
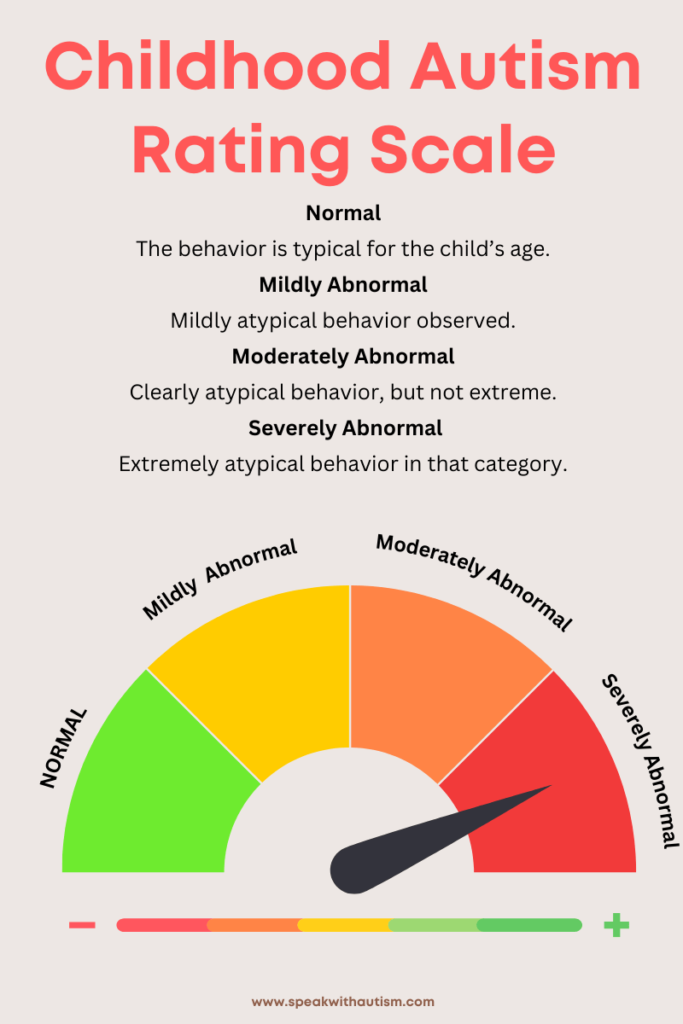
4. CARS (Childhood Autism Rating Scale)
This test is conducted when parents are aware of the severity level of their child’s behavior. It is used to assess moderate to severe behaviors. The test includes 15 categories, and the child is scored on a rating scale from 1 to 4. The highest score in any category indicates that the child’s symptoms are more severe. The child’s overall score is based on these 15 categories.
- social interaction
- imitation
- emotional response
- body use
- object use
- adaptation to change
- visual response
- listening response
- taste, smell, and touch response
- fear and nervousness
- verbal communication
- nonverbal communication
- activity level
- level and consistency of intellectual response
- general impression
5. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales
This test is conducted when the child is of school-going age, and parents need to understand their child’s behavior. It assesses the child’s daily living skills, socialization, and communication. This test is particularly important for children with autism because it focuses on the child’s daily living skills. Parents are also asked questions regarding the child’s daily activities and social communication.
6. SCQ (social communication questionnaire)
The SCQ is a screening tool used for children aged 4 and above. This test is conducted when a child is showing symptoms of autism, but confirmation through screening is needed. Parents are required to answer questions based on the child’s social interaction, language skills, and behaviors. The SCQ is used to evaluate early signs of autism and can be especially important for children whose language development and socialization differ from typical patterns.
7. Screening and Diagnostic Questionnaires for autism
The common tools used for this test are named as:
- ASQ (Autism spectrum Quotient
- ESA (Early Screening of Autism)
“This test is conducted when parents feel the need for a formal diagnosis. The questions asked in this test are related to developmental milestones, and social behaviors, which are helpful for further diagnosis. It is also used for the early detection of children with autism.
8. IQ and Cognitive Testing
This test is useful in distinguishing children with autism or cognitive impairment from those with other mental conditions. It also helps in diagnosing a child’s cognitive strengths and challenges. The purpose of the IQ test is to compare the child’s intellectual abilities with those of children in the same age group. The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is a popular IQ test used to evaluate the cognitive functioning of children. This test is conducted for children aged 6-16 years.
IQ Testing
- These tests test verbal comprehension such as understanding language.
- perceptual reasoning such as solving visual-spatial problems.
- working memory such as remembering and manipulating information.
- processing speed such as how quickly and accurately a child can complete a task.
Cognitive Testing
On the basis of cognitive testing, the challenges faced by children with autism are identified, and appropriate interventions and educational plans are made for them. In this, the child’s mental abilities are assessed separately, such as..
- Attention and concentration: The child’s ability to focus is measured.
- Memory: Both short-term and long-term memory are assessed.
- Executive functioning: Planning, organizing, and problem-solving skills are observed.
- Visual-motor integration: The coordination of visual input with motor actions is evaluated.
9. Sensory Processing Measures (SPM)
This test is preferred when a child has sensory sensitivities or experiences sensory overload. Autism spectrum disorder often involves sensory issues, and children are frequently hypersensitive or hyposensitive to light, touch, and texture. The Sensory Processing Measure (SPM) consists of questions and a checklist that assess the child’s sensory needs.
Conclusion
If you think your child may have autism, initial screening, and proper testing are essential. Early diagnosis is the key to addressing developmental delays effectively. Since every child’s behavior is unique, various autism tests assess behavior, communication, and repetitive patterns. It is important to complete the autism diagnostic process through proper assessment and testing. Children often face behavioral challenges, and by consulting a developmental pediatrician, you can have the appropriate tests conducted for your child. These tests guide the necessary therapies and treatments, helping you address your child’s needs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is M-CHAT scoring?
In the M-CHAT, a child is scored based on the answers to 20 questions. Each “at-risk” response is given 1 point, and the total score determines the risk level:
0-2 Points (Low Risk): No immediate action is needed, but regular monitoring is recommended.
3-7 Points (Medium Risk): A follow-up M-CHAT interview is required for further assessment.
8-20 Points (High Risk): The child should be referred for a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation.
This scoring system helps identify the level of risk and guides the next steps for evaluation or intervention.
What is the Childhood Autism Rating Scale?
This test is conducted when parents are aware of the severity level of their child’s behavior. It is used to assess moderate to severe behaviors. The test includes 15 categories, and the child is scored on a rating scale from 1 to 4. The highest score in any category indicates that the child’s symptoms are more severe.
What is the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC)?
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is a popular IQ test used to evaluate the cognitive functioning of children. This test is conducted for children aged 6-16 years.
These tests test verbal comprehension such as understanding language.
Perceptual reasoning such as solving visual-spatial problems.
Working memory such as remembering and manipulating information.
Processing speed such as how quickly and accurately a child can complete a task.
