In the previous blog, we discussed FDA-approved medications for the treatment of autism. Building on that, in this Blog 2.0, we will explore Effective Off-label Medication Treatment for Autism. As mentioned earlier, autism treatment is categorized into two types: label and off-label treatments.
Table of Contents
Off-Label Medication Treatment for Autism
The treatments are not authorized medications or treatments that have not been approved specifically for autism by the FDA, but doctors prescribe them to control specific symptoms or behaviors in autistic people. These treatments are often used alongside FDA-approved options and require careful doctor supervision and proper consultation.
Label treatments are those that have been approved by the FDA, while off-label treatments are often used in combination with label treatments. If you’d like to know more about label treatments, you can refer to my previous blog.
In this blog, we will focus on off-label treatments. These treatments are designed to address specific behaviors in autistic children and should only be started under the consultation and supervision of a doctor.
Role of Neurotransmitter in Autism
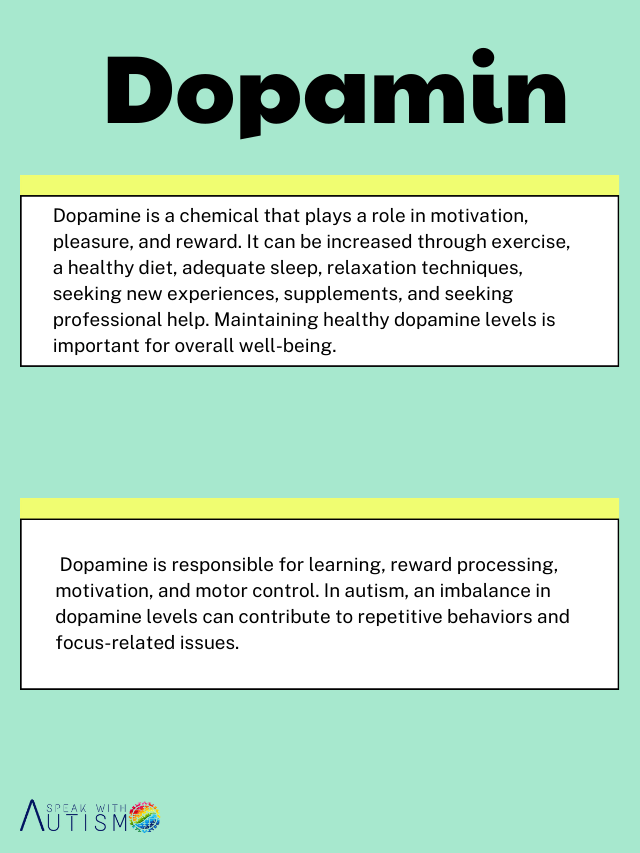
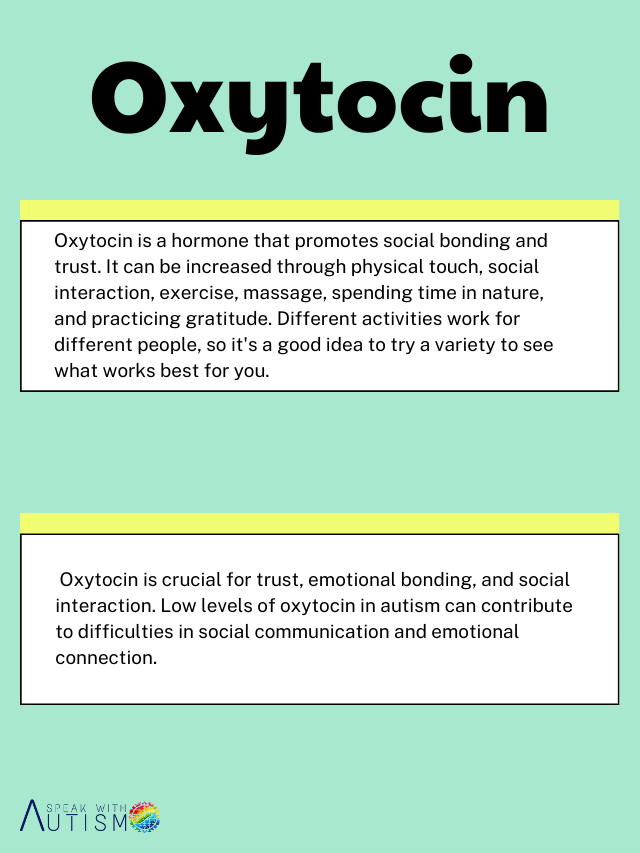
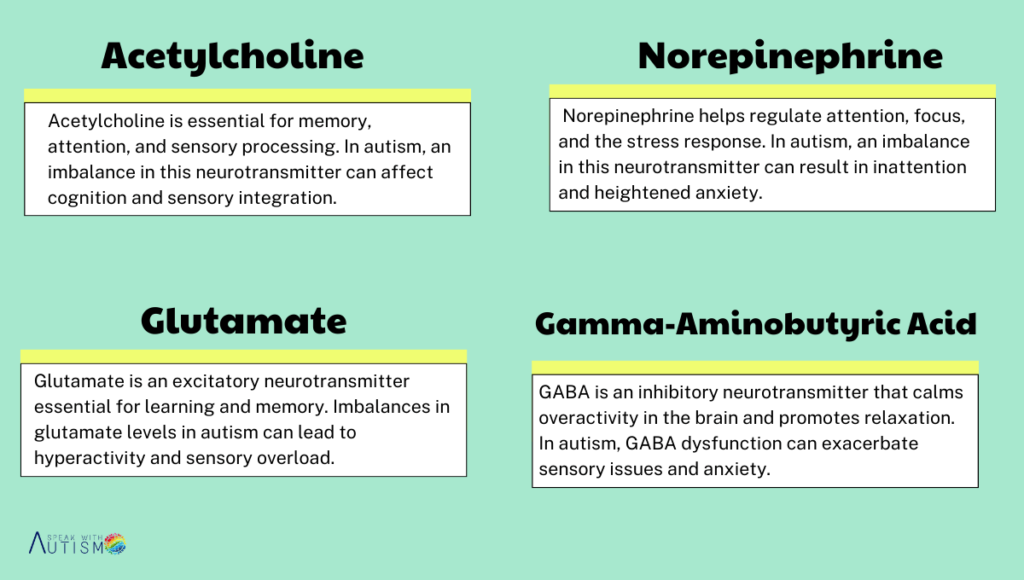
For the treatment of autism, different neurotransmitters are targeted, including dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, acetylcholine, norepinephrine, glutamate, and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). By addressing imbalances in these neurotransmitters, specific behaviors are managed, and appropriate treatments are provided for autistic children. These treatments may include antidepressants, melatonin for sleep regulation, hormones like oxytocin, mood stabilizers, and lipid-based therapies to address various symptoms such as sleep disturbances and mood instability.

Autism Treatments Classification
Autism treatments can be classified as follows:
- Antidepressants-Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI)-Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), Escitalopram
- Antipsychotic (Atypical)- Risperidone (FDA Approved), Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, Olanzapine
- Stimulants and Non-Stimulants- Methylphenidate (Ritalin), Atomoxetine, Adderall (amphetamine/dextroamphetamine)
- Mood Stabilizers-Anticonvulsant- Valproate (Depakote), Lamotrigine
- Anti-Anxiety Medications- Buspirone, Clonazepam
- Sleep Aids- Melatonin
- Anti-seizure medications- Gabapentin, Levetiracetam
- Beta-Blockers-Propranolol
- Gastrointestinal Medications-Probiotics, Laxatives
- Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist- Guanfacine (Intuniv), Clonidine
- Opioid Antagonist- Naltrexone
- Oxytocin Therapy
1. Antidepressants-Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI)
Examples- Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), Escitalopram
SSRIs are prescribed to manage anxiety, repetitive behavior, and depression in autistic children. These medicines block serotonin reuptake and increase its availability, which positively impacts mood and behavior. It has some side effects like nausea, headache, fatigue, appetite changes and sleep disturbances etc.
2. Atypical Antipsychotic
Examples- Risperidone (FDA Approved), Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, Olanzapine
These medications help reduce aggression and violent behavior in autistic children and improve mood and emotional stability. They work by blocking dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, addressing the imbalance of these neurotransmitters. These medications help calm overactive brain signals in autistic individuals with irritability and social difficulties, However, they can have side effects, such as weight gain, drowsiness, hormonal changes, and motor problems.
3. Stimulants and Non-Stimulants
Examples- Methylphenidate (Ritalin), Atomoxetine, Adderall (amphetamine/dextroamphetamine)
These medicines help improve attention span, reduce impulsivity, and enhance focus and self-regulation. Stimulants work by increasing the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, while non-stimulants block their reuptake. These medicines are prescribed for autism when ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) symptoms are also present. However, they may have some side effects, such as sleep problems, loss of appetite, mood swings, and irritability.
4. Mood Stabilizers– Anticonvulsants
Examples-Anticonvulsant- Valproate (Depakote), Lamotrigine
These medicines help stabilize aggression, irritability, impulsive behaviors, and extreme mood changes in autistic children. They work by controlling abnormal electrical activity in the brain and enhancing the neurotransmitter GABA, which promotes mood and neural stability. However, these medicines can have side effects, such as weight gain, drowsiness, dizziness, and, in rare cases, liver toxicity.
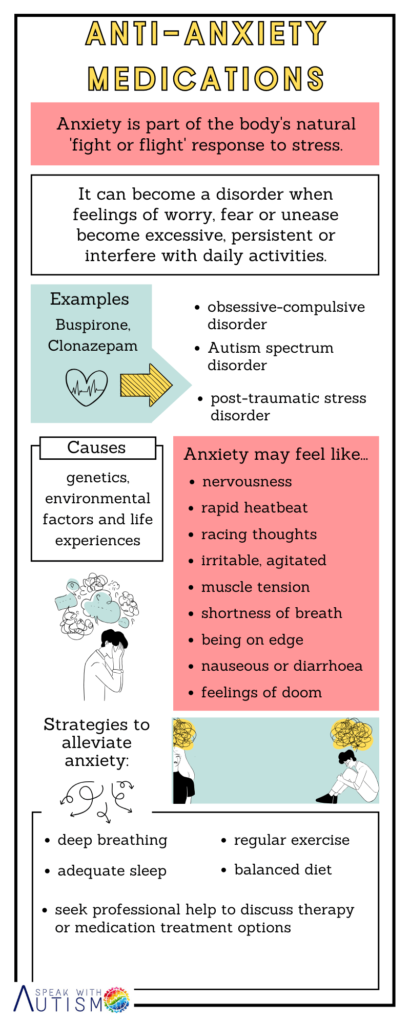
5. Anti-Anxiety Medications
Examples- Buspirone, Clonazepam
These medicines help reduce anxiety, social fears, and panic attacks in autistic children, promoting better sleep and relaxation. Buspirone works by acting on serotonin receptors, while Clonazepam calms the nervous system by increasing GABA activity. However, these medicines may have side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and long-term use can lead to a risk of dependency. Some natural ways can be used to reduce anxiety in autistic children which are provided in the picture.
6. Sleep Aids
Examples- Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone that helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and reduces bedtime resistance. Sleep problems are common in autistic children, and melatonin supports the brain’s natural sleep signals, making it easier for children to fall asleep. It helps with quicker sleep onset, better sleep quality, and fewer night awakenings. However, some side effects, like vivid dreams or daytime drowsiness, can occur but are rare. Some natural ways can be used to induce sleep in autistic children which are provided in the picture.

7. Anti-seizure medications
Examples- Gabapentin, Levetiracetam
Gabapentin and Levetiracetam are used when epilepsy and autism overlap. These medicines help by calming mood and reducing aggression. They work by stabilizing abnormal electrical signals in the brain, controlling seizures, and managing repetitive behaviors. Some common side effects include drowsiness, fatigue, and mood changes.
8. Beta-Blockers
Examples- Propranolol
Propranolol is a beta-blocker used to improve social interactions in autism and reduce aggression, anxiety, and social stress. It helps by lowering physical symptoms like a fast heartbeat and trembling. Propranolol works by blocking stress hormones like adrenaline, calming both the brain and body. However, it may cause side effects such as low blood pressure and dizziness.
9. Gastrointestinal Medications
Examples- Probiotics, Laxatives
Probiotics improve gut health and support better digestion, which helps reduce discomfort in autistic children. They can enhance mood and behavior and also regulate bowel movements. Many autistic children experience issues like diarrhea or constipation, which can be managed effectively with the use of probiotics.
10. Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist
Examples- Guanfacine (Intuniv), Clonidine (Arkamin)
The benefits of Guanfacine (Intuniv) and Clonidine include reduced hyperactivity, better impulse control, improved sleep, and better focus. These medicines are helpful for children with overactive or disruptive behaviors. They work by calming the brain through their action on adrenergic receptors. However, they may have side effects like low blood pressure and fatigue.
11. Opioid Antagonist
Examples- Naltrexone
Naltrexone is used to manage self-injury, irritability, and severe aggression. It works by blocking opioid receptors in the brain, helping to control these behaviors. Some common side effects include nausea and dizziness.
12. Oxytocin Therapy
Oxytocin is prescribed to help improve eye contact, communication, and social responses in children with autism. This therapy is particularly helpful in cases where social difficulties are more prominent. However, it may have some side effects, such as mild irritation or headaches.
Conclusion
In autism, an imbalance of neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), and glutamate plays a major role. These neurotransmitters directly affect sensory issues, repetitive behaviors, mood swings, and social communication difficulties.

Proper therapies such as speech therapy, sensory therapy integration, occupational therapy, and ABA (applied behavior analysis) therapy, along with medications like Risperidone, Aripiprazole, Stimulants, and SSRIs (Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), help target this imbalance and improve symptoms. All medications should be used under a doctor’s supervision to ensure a safe and effective treatment plan. Following proper therapies and treatments can help autistic children develop life skills and progress in a safe manner. Additionally, boosting happy hormones through positive activities can be beneficial for your loved ones which we provided in detail in the picture.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What medications are used to treat autism?
Risperidone and aripiprazole, which are FDA-approved medications, are used for the treatment of autism and are considered labeled medicines. On the other side off-label medications, which are not approved by the FDA, are used in combination with labeled medicines. These include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), stimulants, mood stabilizers, sleep aids etc.
Can medications be stopped once the child shows improvement?
Medication for autism should never be stopped or altered without consulting a doctor. Children often respond well to medication, but it is essential to adjust the medication over time. Without proper adjustments, changes in medication can worsen the child’s behavior. Parents should not stop or reduce the dosage without consulting a doctor. Even if the doctor recommends stopping the medication, it’s important to discuss the child’s behavior with the doctor first. If the doctor observes no effect from the medication, they will gradually reduce the dose and eventually stop it. Neurologists typically adjust the dose or change the medication based on the child’s overall progress and behavior.
Are there natural and alternative treatments for autism?
Many natural and alternative treatments for autism should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. These treatments are used alongside other therapies to manage symptoms and improve life skills in children. One such treatment is dietary intervention, which includes focusing on gluten-free-casein-free diets that is the GFCF diet, and making nutritional changes. You can also improve brain function with supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and other vitamins. Some parents have reported positive effects from these supplements. Additionally, therapies like occupational therapy, aromatherapy, behavior therapy, sensory integration therapy, applied behavior analysis therapy, and music therapy can help improve your child’s health.

Pingback: Does Adderall Help Autism? Discover its Facts