World Treats Autism- To answer which treatments for autism are most preferred in foreign countries, we will focus on therapies and approaches that are internationally popular and research-based. Below are some of the main treatments that are commonly used in foreign countries for the management of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)

Table of Contents
How the World Treats Autism
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- What is: This is a behavior-based therapy that improves social, communication, and daily living skills through positive reinforcement.
- Where is Popular: This is most preferred in the United States, Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom. It is evidence-based and is considered the gold standard for autism.
- Benefit: Helps reduce children’s repetitive behaviors and increase social interaction.
2. Speech and Language Therapy
- What is: Works on communication skills, such as speaking, understanding, or using non-verbal cues.
- How Popular: In countries like the United States, UK, Germany, and the Netherlands, this therapy is common for children with communication challenges along with autism.
- Benefit: Improves verbal and non-verbal communication.
3. Occupational Therapy (OT)
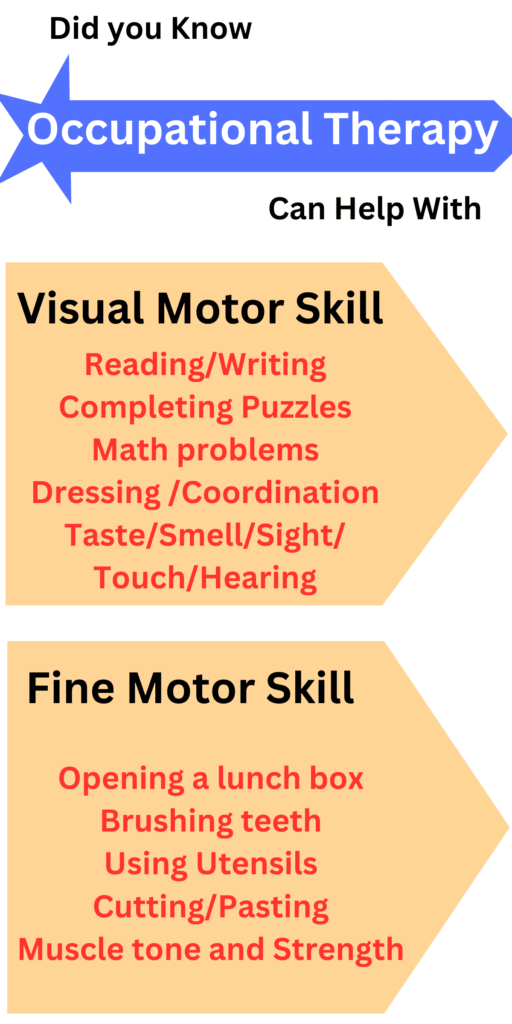

- What is: It focuses on sensory processing issues and daily activities (like getting dressed or writing).
- Where Popular: It is most commonly used for sensory integration in Australia, Canada, Sweden, and Israel.
- Benefits: It helps manage sensory sensitivities, often seen in autism.
4. Sensory Integration Therapy
- What is: This therapy addresses sensory processing difficulties, like discomfort with loud sounds or textures.
- Where Popular: It is most popular in Germany, the United States, and Nordic countries (like Sweden and Norway).
- Benefit: Improves emotional regulation by balancing over- or under-sensitivity.
5. Stem Cell Therapy
- What is: This is an experimental treatment in which stem cells are used to improve brain function or neural connectivity.
- Where Popular: It is emerging in countries like Mexico, India, Turkey, and Austria. Clinical trials are also underway in the United States.
- Benefit: Some studies have shown improvements in communication and behavior, but it is not yet fully proven and can be risky.
6. Social Skills Training
- What is: These are group-based or individual sessions that focus on social interactions and peer relationships.
- Where is Popular: Common in school programs or therapy centers in the UK, Canada, and the Netherlands.
- Benefits: Improves ability to interact with friends and understand social cues.
7. Medication
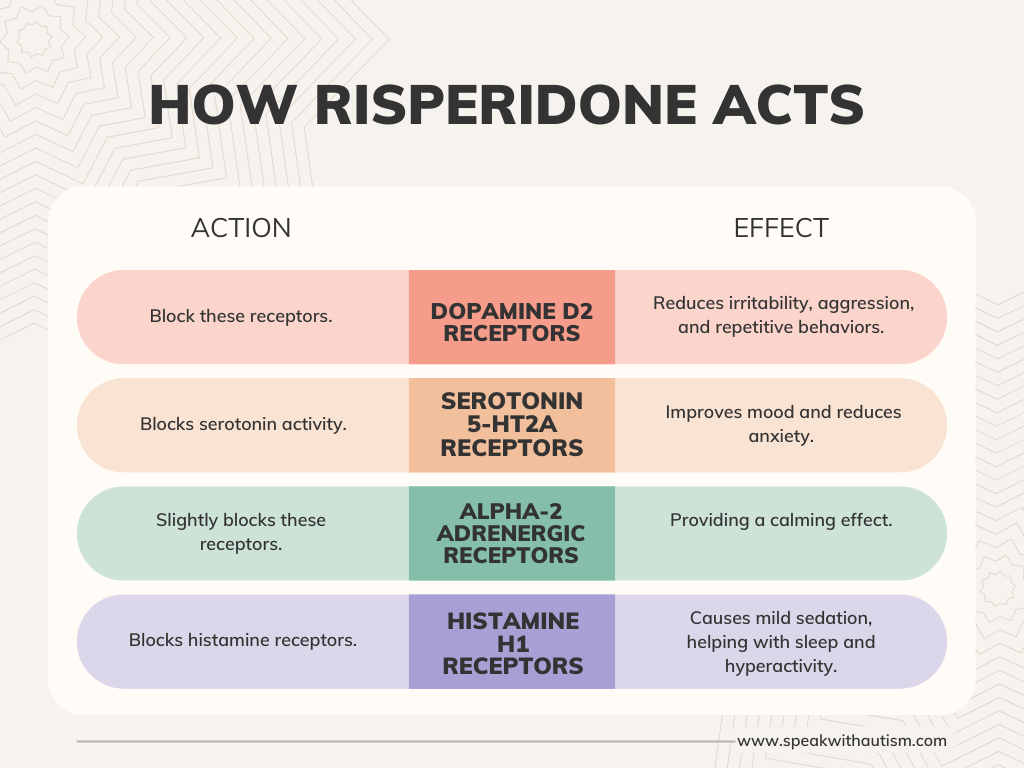
- What is: There is no specific medication for autism, but antipsychotics (such as Risperidone) or stimulants (such as Methylphenidate) are used to manage symptoms such as anxiety, aggression, or hyperactivity.
- Where Popular: Doctors use them cautiously in the United States, Germany, and Singapore.
- Benefit: It can control symptoms, but monitoring for side effects is important.
8. Animal-Assisted Therapy (Pet Therapy)

- What Is: It works on emotional bonding and sensory regulation through interaction with dogs, horses (hippotherapy), or dolphins.
- Where Popular: It is popular in Germany (hippotherapy), United States, and Israel.
- Benefit: Helps in forming emotional connection and reducing stress.
9. Developmental, Individual-Difference, Relationship-Based Model (DIR/Floortime)
- What is: This is a play-based approach that focuses on the child’s emotional and developmental needs.
- Where Popular: Popular among parents and therapists in the United States and Canada.
- Benefits: Increases bonding and communication through the child’s natural interests.
10. Early Intervention Programs
- What is: These are comprehensive programs for young children (usually 2-5 years old) that combine ABA, speech therapy, and OT (occupational therapy).
- Where Popular: These are government-supported in Australia (through the NDIS), Sweden, and the UK.
- Benefit: Starting early leads to better long-term outcomes.
11. Play therapy and art therapy

In countries like France, Italy and Japan, play and art therapy are very popular for children. This treatment gives children a chance to express their feelings through games, painting or music. It is especially useful for those children who cannot express themselves verbally. This therapy is fun as well as helps in emotional development.
12. Parent-mediated intervention
In countries like the Netherlands and Switzerland, parents are involved in the treatment of children by giving them training. In this, parents are taught special techniques so that they can work with children at home on behavior improvement and increasing communication. This method is both economical and effective.
Countries and Their Special Approaches
- United States: Hub of ABA and research-based therapies, with top centers like UCLA Autism Center.
- Australia: Personalized funding and therapies through the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS).
- Germany: Focus on stem cell research and regenerative medicine, along with behavioral therapy.
- Mexico: A major destination for affordable stem cell therapy.
- Sweden/Netherlands: Inclusive education and sensory-friendly environments
Conclusion
Treatments for autism in foreign countries are chosen according to individual needs. Evidence-based options such as ABA, speech therapy, and occupational therapy are most common, while new approaches such as stem cell therapy are also emerging.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Which country has the highest success rate for the treatment of autism?
It is difficult to definitively pinpoint a single country for the highest success rates in autism treatment because it depends on individual outcomes and available data. But the United States is often considered the top country because Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is very advanced there and research institutions like the UCLA Center for Autism and the Kennedy Krieger Institute provide world-class treatments. Early intervention programs and insurance coverage are also widespread there, which increases success rates. Canada and Australia are also notable for their comprehensive healthcare systems and early intervention. Nordic countries like Sweden are known for inclusive education and sensory-friendly approaches. Early diagnosis, tailored therapies, and family support play a major role in high success rates.
Which country has the lowest success rate for the treatment of autism?
It is difficult to say which country has the lowest success rate in autism treatment because success rate data is not uniformly available for every country. But, if we look at prevalence and treatment access, low- and middle-income countries like Somalia or Afghanistan may have lower success rates of autism treatment. In these countries, healthcare infrastructure is poor, autism awareness is low, and access to specialized therapies like ABA or occupational therapy is difficult. According to studies, in some parts of Africa and Asia, outcomes are not better due to a lack of diagnosis and treatment resources. In Somalia, the prevalence is shown to be 2.07%, but treatment facilities are almost nonexistent. In such countries, cultural stigma and lack of trained professionals also affect the success rate. In contrast, in developed countries, the success rate is higher due to better resources.
